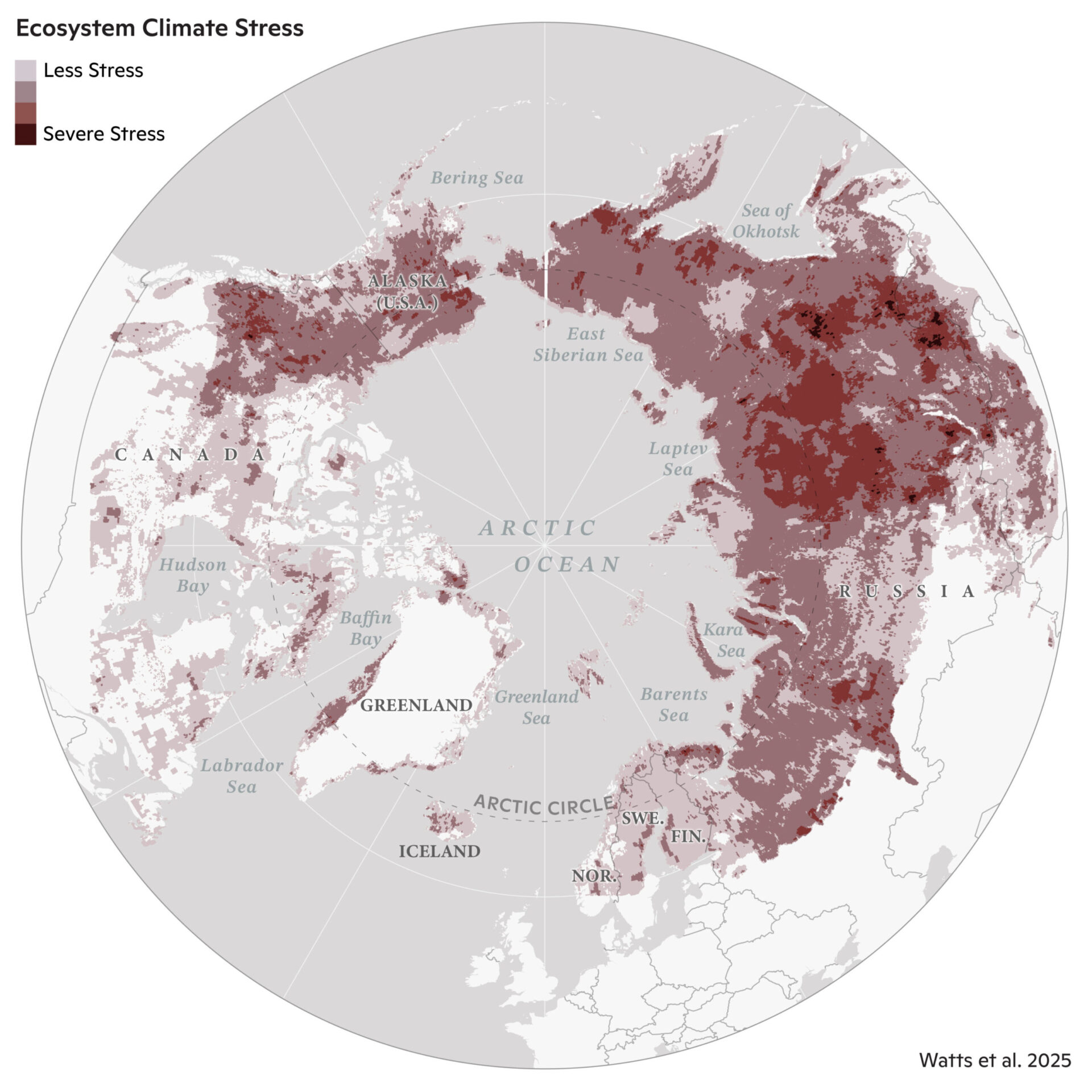
Ecological warning lights have blinked on throughout the Arctic over the past 40 years, in keeping with new analysis, and most of the fastest-changing areas are clustered in Siberia, the Canadian Northwest Territories, and Alaska.
An evaluation of the quickly warming Arctic-boreal area, revealed in Geophysical Analysis Letters, gives a zoomed-in image of ecosystems experiencing a few of the quickest and most excessive local weather modifications on Earth.
Lots of the most climate-stressed areas function permafrost, or floor that stays frozen year-round, and has skilled each extreme warming and drying in latest a long time.
To determine these “hotspots,” a group of researchers from Woodwell Local weather Analysis Heart, the College of Oslo, the College of Montana, the Environmental Techniques Analysis Institute (Esri), and the College of Lleida used greater than 30 years of geospatial information and long-term temperature data to evaluate indicators of ecosystem vulnerability in three classes: temperature, moisture, and vegetation.
Constructing on assessments just like the NOAA Arctic Report Card, the analysis group went past evaluating remoted metrics of change and checked out a number of variables directly to create a extra full, built-in image of local weather and ecosystem modifications within the area.
“Local weather warming has put quite a lot of stress on ecosystems within the excessive latitudes, however the stress seems to be very totally different from place to put and we wished to quantify these variations,” mentioned Dr. Jennifer Watts, Arctic program director at Woodwell Local weather and lead creator of the research.
“Detecting hotspots on the native and regional stage helps us not solely to construct a extra exact image of how Arctic warming is affecting ecosystems, however to determine locations the place we actually must focus future monitoring efforts and administration assets.”
The group used spatial statistics to detect “neighborhoods,” or areas of notably excessive ranges of change through the previous decade.
“This research is precisely why we have now developed these sorts of spatial statistic instruments in our expertise. We’re so proud to be working intently with Woodwell Local weather on figuring out and publishing these sorts of vulnerability hotspots that require efficient and speedy local weather adaptation motion and long-term coverage,” mentioned Dr. Daybreak Wright, chief scientist at Esri. “That is basically what we imply by the ‘Science of The place.'”
The findings paint a fancy and regarding image.
Essentially the most substantial land warming between 1997–2020 occurred within the far japanese Siberian tundra and all through central Siberia. Roughly 99% of the Eurasian tundra area skilled vital warming, in comparison with 72% of Eurasian boreal forests.
Whereas some hotspots in Siberia and the Northwest Territories of Canada grew drier, the researchers detected elevated floor water and flooding in components of North America, together with Alaska’s Yukon-Kuskokwim Delta and central Canada. These will increase in water on the panorama over time are doubtless an indication of thawing permafrost.
-

Warming severity “hotspots” in Arctic-boreal area between 1997-2020 had been detected by analyzing a number of variables together with satellite tv for pc imagery and long-term temperature data. Watts et al., 2025, Geophysical Analysis Letters. Credit score: Christina Shintani / Woodwell Local weather Analysis Heart
-

Map of areas of extreme to extraordinarily extreme drying within the Arctic-boreal area. Drying severity was decided by analyzing a number of variables from the satellite tv for pc report. Watts et al., 2025, Geophysical Analysis Letters. Credit score: Christina Shintani / Woodwell Local weather Analysis Heart
-

Map of areas that skilled vegetation local weather stress within the Arctic-boreal area between 1997-2020 as detected by a number of variables from the satellite tv for pc report. Watts et al., 2025, Geophysical Analysis Letters. Credit score: Christina Shintani / Woodwell Local weather Analysis Heart
Among the many 20 most weak locations the researchers recognized, all contained permafrost.
“The Arctic and boreal areas are made up of various ecosystems, and this research reveals a few of the advanced methods they’re responding to local weather warming,” mentioned Dr. Sue Natali, lead of the Permafrost Pathways mission at Woodwell Local weather and co-author of the research.
“Nonetheless, permafrost was a standard denominator—essentially the most climate-stressed areas all contained permafrost, which is weak to thaw as temperatures rise. That is a extremely regarding sign.”
For land managers and different decisionmakers, native and regional hotspot mapping like this could function a extra helpful monitoring instrument than region-wide averages. Take, for example, the instance of COVID-19 monitoring information: maps of county-by-county wastewater information are typically extra useful instruments to information resolution making than nationwide averages, since charges of illness prevalence and transmission can range extensively amongst communities at a given second in time.
So, too, with local weather tendencies: native information and pattern detection can help administration and adaptation approaches that account for distinctive and shifting situations on the bottom.
The numerous modifications the group detected within the Siberian boreal forest area ought to function a wakeup name, mentioned Watts.
“These forested areas, which have been serving to take up and retailer carbon dioxide, at the moment are exhibiting main local weather stresses and growing danger of fireside. We have to work as a worldwide neighborhood to guard these vital and weak boreal ecosystems, whereas additionally reining in fossil gas emissions.”
Extra info:
Regional Hotspots of Change in Northern Excessive Latitudes Knowledgeable by Observations From House, Geophysical Analysis Letters (2025). DOI: 10.1029/2023GL108081
Offered by
Woodwell Local weather Analysis Heart
Quotation:
Arctic hotspots research reveals areas of local weather stress in Northern Alaska and Siberia (2025, January 16)
retrieved 17 January 2025
from https://phys.org/information/2025-01-arctic-hotspots-reveals-areas-climate.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.